Cardiac imaging Made Easy, Master the Heartbeat
- Radiology is a vital component of modern medicine, crucial for the diagnosis, treatment, and management.
- Radiology is committed to contributing to high-quality healthcare through patient care, education, and research.
- The aim of the current study is to develop a novel approach for 2D breath‐hold cardiac cine imaging from a single heartbeat, by combining cardiac motion‐corrected reconstructions and non-rigidly aligned patch‐based regularization.
- Conventional cardiac cine imaging is obtained via motion‐resolved reconstructions of data acquired over multiple heartbeats.
Introduction
The professional practice of computed tomography requires specific knowledge and skills generally not obtained in basic education programs in radiography. The curriculum is intended as a guide to establish criteria for educational programs in computed tomography. It provides candidate with a structured program containing the necessary elements to produce graduates with superb knowledge and skills in computed tomography. Upon completion of this curriculum, graduates should be able to perform computed tomography with a high level of proficiency.
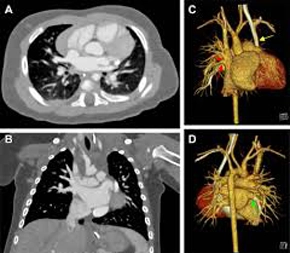
What it's Used For:
CT scans are valuable tools for diagnosing a wide range of medical conditions and for guiding various medical procedures. Some common uses include:
- Detecting and Diagnosing:
- Cancers (locating tumors, assessing their size and spread).
- Infections.
- Blood clots.
- Internal bleeding.
- Bone fractures and disorders.
- Soft tissue injuries.
- Vascular diseases.
- Guiding Procedures:
- Biopsies (taking tissue samples).
- Drainage of abscesses.
- Radiation therapy planning.
- Surgical planning.
- Monitoring Treatment: Assessing how well treatments, such as cancer therapy, are working.
- Emergency Situations: Quickly identifying internal injuries after trauma, such as car accidents or strokes.
- Detecting and Diagnosing:
CT-SCAN COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY
is a sophisticated medical imaging technique that utilizes X-rays and computer processing to create detailed cross-sectional images inside of your body.
ACTVET APPROVED # ACT-51024
Registration Details
- Duration: 2 days
- Date: 21, 22th June 2025
- Timing: 10.00 AM to 5.00 pm
- Location: ARAMTEC. Abu Dhabi – Al Danna Zoon
- Fee: 3500 AED
Don’t miss this opportunity to elevate your skills and connect with pioneers in cardiac imaging. Register now and take a step closer to mastering CT cardiac imaging.
The member is awarded:
- A certificate from the ARAMTEC, accredited by the ACTVET, ABU DHABI Government
- A certificate and membership from CHHS, a global medical organization, UK
How does it work?
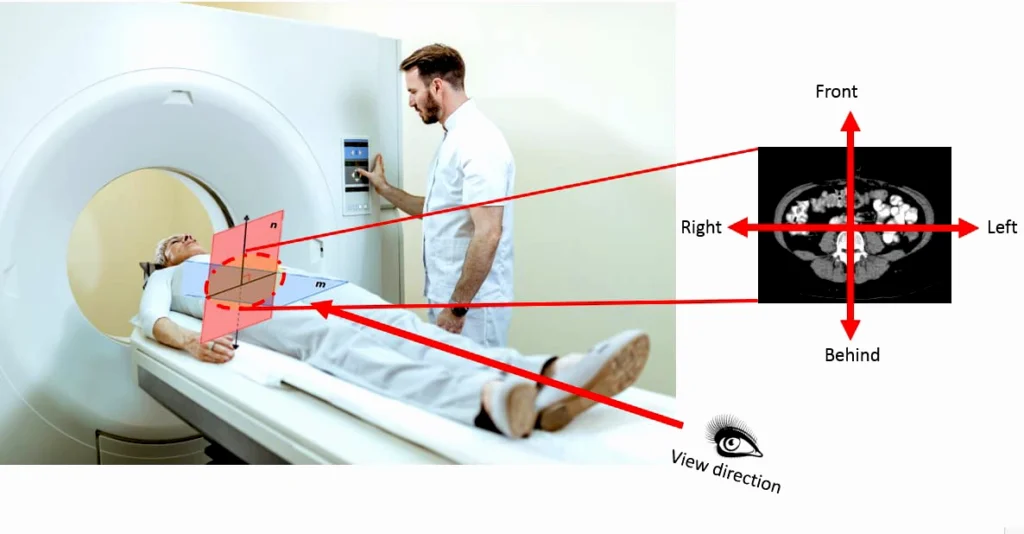
- X-ray Source and Detectors: A motorized X-ray tube rotates around your body while you lie on a table that slowly moves through a donut-shaped scanner (gantry). Opposite the X-ray source are digital detectors that measure the amount of X-rays that pass through your tissues.
- Multiple Angles: Unlike a standard X-ray that takes a single image, a CT scanner captures numerous images from different angles as the X-ray tube revolves.
- Computer Processing: The detectors send the information to a powerful computer. Using complex mathematical algorithms, the computer processes this data to create cross-sectional images, often called “slices.”
- Image Display: These slices can be viewed individually or stacked together to generate detailed two-dimensional or even three-dimensional images of bones, soft tissues, organs, and blood vessels.
Who should take this course?
- Radiologist
- Cardiologists.
- Medical imaging student.
- Radiologic Technologist.
- Radiologist resident.
Course Highlights:
- Advanced training in CT cardiac imaging techniques
- Hands-on sessions with cutting-edge imaging technology
- Interpretation of complex cardiac cases
- Protocol optimization and radiation dose management
- Case studies and real-world applications
- Networking with industry leaders
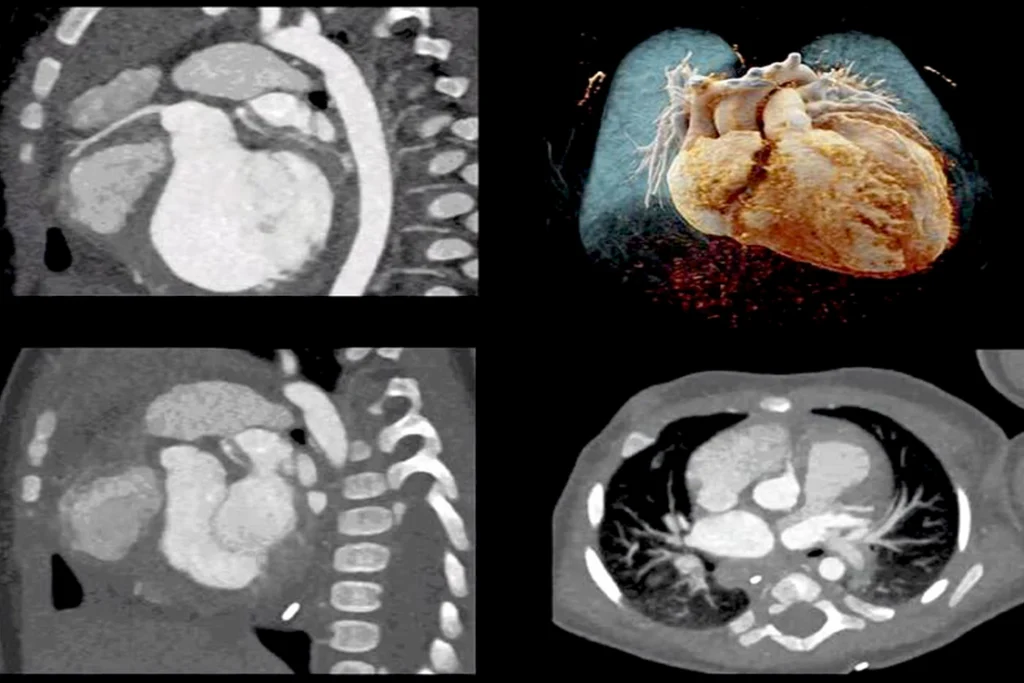
Introduction to CT Cardiac Imaging
- Introduces the fundamental principles of CT technology and its application to cardiac imaging.
- Focuses on the unique challenges and opportunities of imaging the moving heart.
- Compares and contrasts cardiac CT with other cardiac imaging modalities (echocardiography, nuclear cardiology, MRI).
- Highlights the specific advantages of CT in certain clinical scenarios.
- Covers the historical development of cardiac CT.
- Explains its current role in cardiovascular diagnostics.
- Outlines the basic physics behind CT image generation.
- Provides an overview of different types of CT scanners used in cardiac imaging.
- Aims to provide a solid understanding of the value and potential applications of cardiac CT.
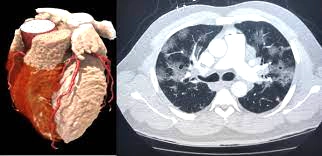
Anatomy and Pathology by CT
- Focuses on detailed visualization of normal cardiac anatomy using CT scans.
- Covers identification of all four chambers, coronary arteries and branches, cardiac veins, pericardium, and great vessels.
- Transitions to recognizing various cardiac pathologies on CT images.
- Includes the appearance of coronary artery disease (stenosis, calcification, stents, bypass grafts).
- Covers different types of cardiomyopathies (hypertrophic, dilated, restrictive).
- Includes congenital heart defects and valvular heart disease.
- Covers cardiac masses and tumors, and pericardial diseases.
- Emphasizes understanding the characteristic CT features of each condition.
- Aims to enable differentiation between normal and abnormal cardiac CT findings.
Image Acquisition and Optimization
- Delves into the technical aspects of acquiring high-quality cardiac CT images.
- Explains different scanning protocols (axial, helical, high-pitch spiral) and their applications.
- Focuses on electrocardiogram (ECG) gating and its role in minimizing motion artifacts.
- Covers prospective and retrospective ECG gating techniques and their implications.
- Explores strategies for optimizing image parameters (kVp, mAs, collimation, pitch).
- Aims to achieve optimal image resolution while adhering to the ALARA principle.
- Discusses factors affecting image quality (patient size, heart rate variability, metallic implants).
- Covers techniques to mitigate these image quality issues.
Post-Processing and Interpretation
- Equips you with skills to manipulate and analyze raw CT data for clinical information.
- Covers post-processing techniques: multiplanar reconstructions (MPR), maximum intensity projections (MIP), and volume rendering.
- Guides you through a systematic approach to interpreting cardiac CT images.
- Includes assessing image quality and identifying normal and abnormal findings.
- Covers quantifying coronary artery stenosis and evaluating cardiac function.
- Includes recognizing incidental findings.
- Teaches principles of structured reporting.
- Aims to enable effective communication of findings to referring physicians.
Radiation Safety and Dose Management
- Covers the fundamental principles of radiation physics and potential risks.
- Explains factors contributing to radiation dose in cardiac CT.
- Details techniques for minimizing radiation dose (scanning parameters, ECG gating, iterative reconstruction, dose modulation).
- Emphasizes the importance of the ALARA principle and appropriate shielding.
- Covers documenting radiation dose.
- Introduces relevant guidelines and recommendations for radiation safety in cardiac imaging.
Clinical Applications and Case Studies
- Explores the diverse clinical applications of cardiac CT through real-world cases.
- Illustrates the use of CT in diagnosis, risk stratification, and management of cardiovascular diseases.
- Includes the role of CT coronary angiography (CTCA) for chest pain and suspected CAD.
- Covers assessment of coronary artery bypass grafts and stents.
- Includes imaging congenital heart disease in adults.
- Covers evaluation of cardiac masses and thrombi.
- Includes planning transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI).
- Covers assessment of the pericardium.
- Aims to develop the ability to integrate knowledge, recognize pathology, and understand the clinical impact of CT findings.
Cardiac imaging Made Easy, Master the Heartbeat of Radiology
أساسيات التصوير القلبي الدقيق من الأساس الى الإحتراف
Introduction
The professional practice of computed tomography requires specific knowledge and skills generally not obtained in basic education programs in radiography. The curriculum is intended as a guide to establish criteria for educational programs in computed tomography. It provides candidate with a structured program containing the necessary elements to produce graduates with superb knowledge and skills in computed.
The aim of the current study is to develop a novel approach for 2D breath‐hold cardiac cine imaging from a single heartbeat, by combining cardiac motion‐corrected reconstructions and non-rigidly aligned patch‐based regularization. Conventional cardiac cine imaging is obtained via motion‐resolved reconstructions of data acquired over multiple heartbeats.
Why CT-scan?
- A noninvasive way to study all parts of your body
- Less sensitive to movement than MRI
- Help doctors plan for, and later assess the results of many surgeries.
- Its ability to image bone, soft tissue and blood vessels all at the same time
- To further look at an abnormality seen on another test such as an x-ray or an ultrasound
